PLM Software: why every fashion company should have one
What is a PLM?
There are multiple definitions for PLM software that can vary widely since the processes underlying the product lifecycle management and the supported requirements differ significantly depending on the industrial sector. PLM is the acronym of Product Lifecycle Management, and can be defined as the set of data and processes supporting the design, development and management of products throughout their life cycle from their conception through their design and production, including also distribution and sale phases.
PLM is a collaborative process that involves many – if not all – internal company resources, as well as supplier partners and third parties. Focusing only on clothing, today the PLM software involves the retailer, the owner of the brand, who produces the garment, who manufactures the fabric, business partners and many other figures involved in the life cycle of the product. There are now dozens of dealers in the world that offer PLM software platforms for various industries and some of these, although not yet many compared to the overall landscape, have been developed ad hoc for the clothing and packaging industry.

What are the fundamental characteristics of PLM?
A PLM software was created for the collection and organization of data relating to a product in the various phases of conception, design, production, distribution, assistance and obsolescence of a product.
A summary but clarifying classification of software programs used in the industrial production is that which distinguishes between programs that generate content than those who manage content. PLM software is, in a sense, the link between these two categories of programs.
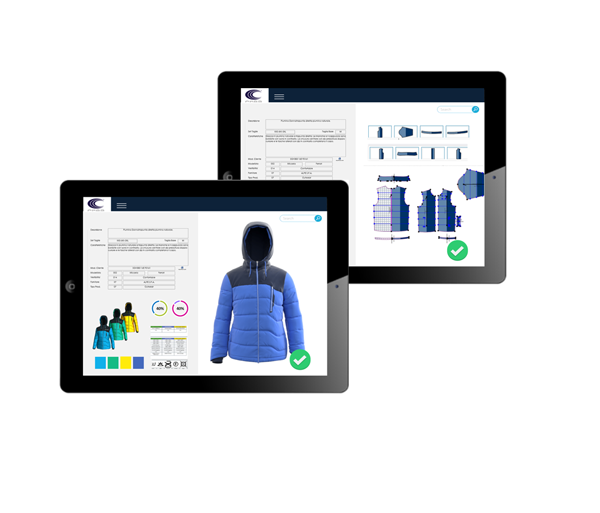
A fundamental aspect is therefore its integration with other programs that assist both management and product creation. First of all, it can be integrated with office-type programs, such as Microsoft ™ Office, to view and manage documents, tables and spreadsheets containing analyzes, statistics, product specifications during the design phase, or technical documentation relating to the product already created. It can be integrated with programs containing style drafts and drawings and with Computer-Aided Design and Computer-Aided Manufacturing (CAD / CAM) systems (Want to know more about all the advantages of the integration between CAD and PLM? Then, read this article!) used for the design of patterns or plotting and automatic cutting plots. And with collaboration and file sharing software, e.g. Microsoft ™ SharePoint, or e-mail communication, e.g. Microsoft ™ Outlook. In general, a complete integrability of the PLM software allows to reach all data and information, all the technical and commercial documentation related to the life cycle of the product itself.
What are all the advantages of a PLM software?
- It guarantees easy archiving of documents, no longer necessarily linked to the storage of files on hard disk or USB sticks. All PLM systems allow to maintain and update database information such as Microsoft ™ SQL Server, Oracle ™ or mySQL.
- Guarantees the traceability of each document through unique codings assigned to the document itself.
- Allows quick access to documents through the relevant unique identification codes, or through customizable and rapid search interfaces.
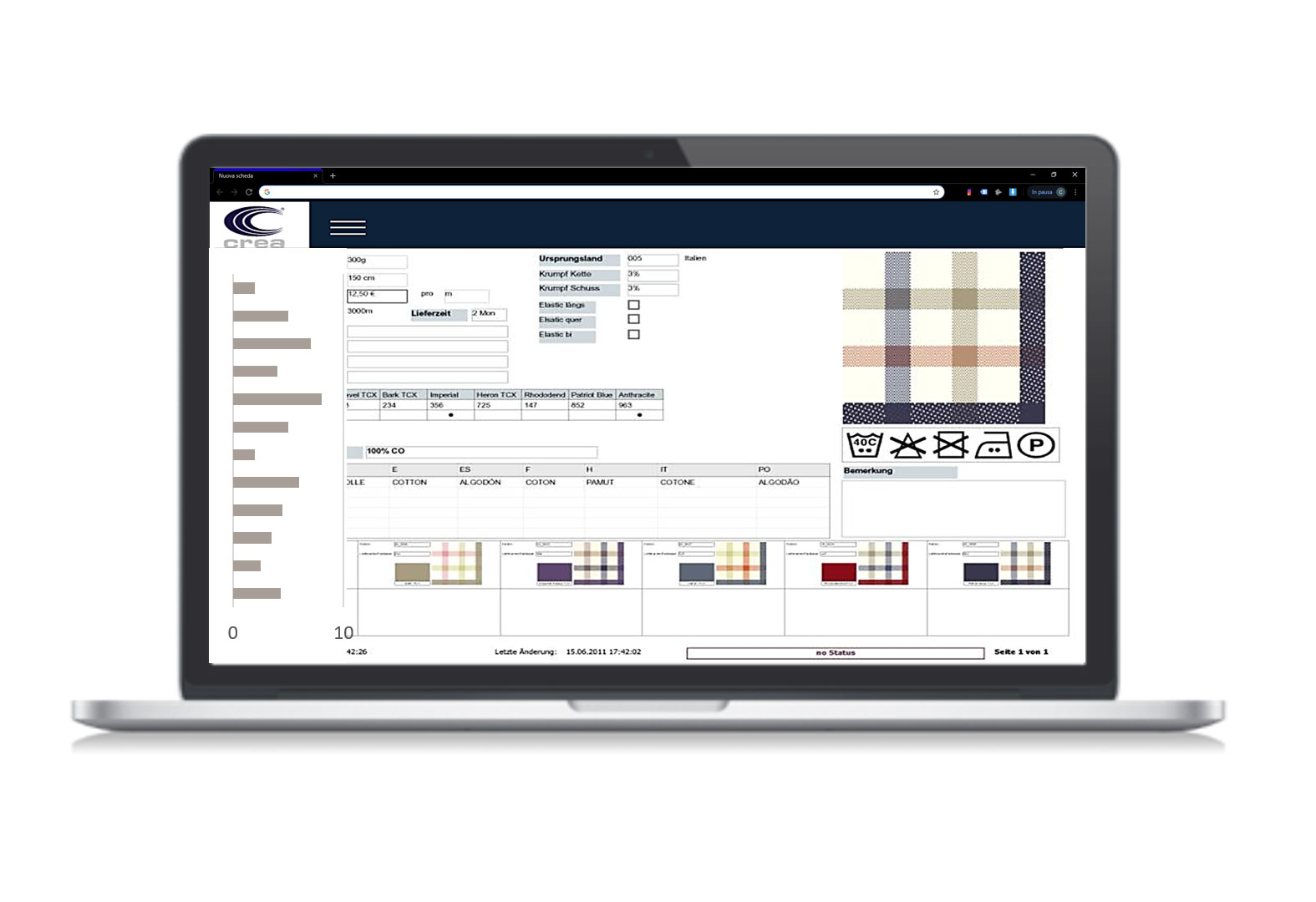
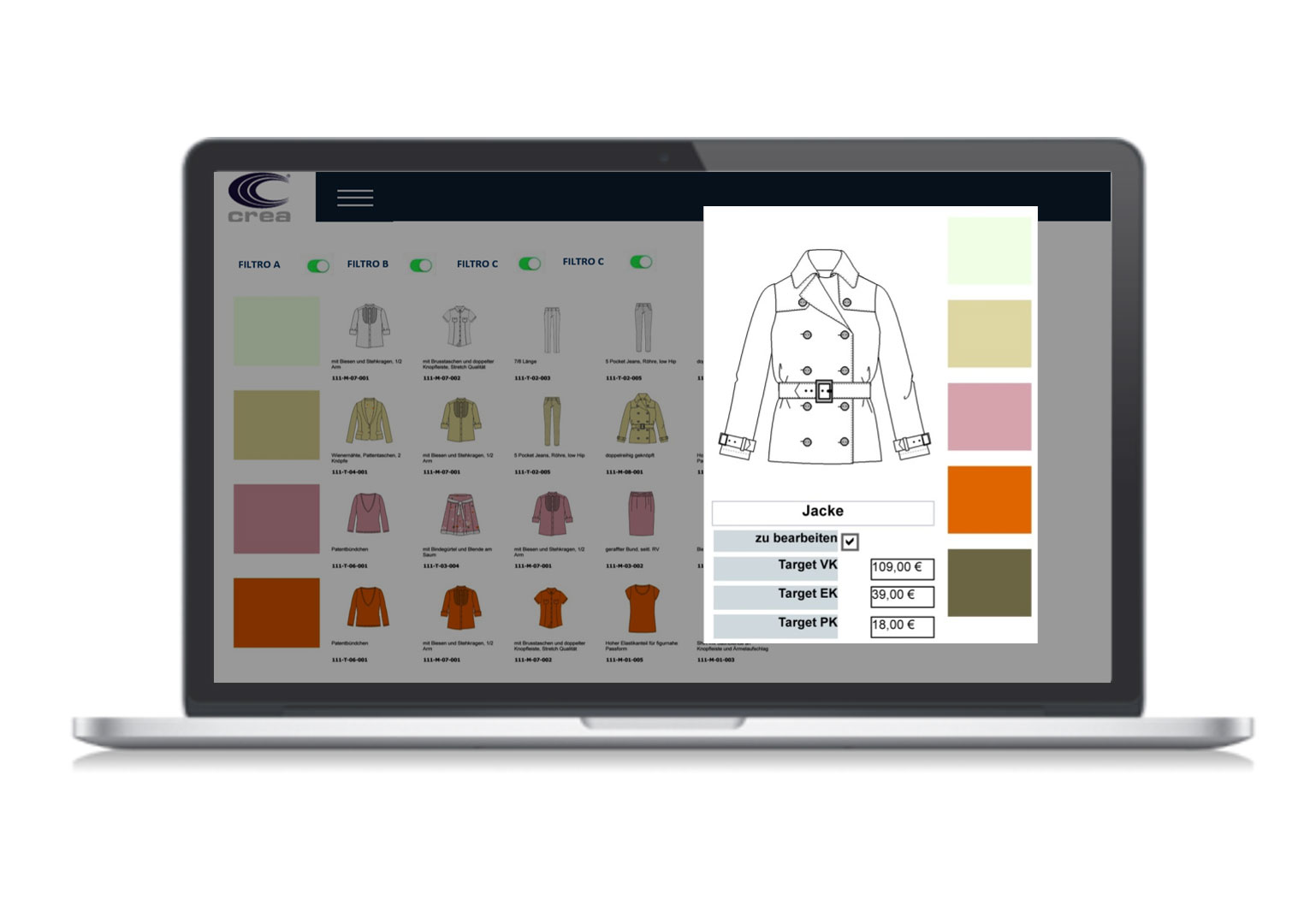
- Allows a search of the document through the so-called metadata of this. Metadata can be seen as information that is not necessary in terms of content, but which nonetheless helps in aspects of management and research of the document itself, and which facilitate communication between the various actors involved in the product life cycle. In the specific case of the technical design the metadata are identified with the data included in the registration table, also called title block, or in the case of technical data sheets information such as the author, the date of last modification or last access can facilitate communication between departments.
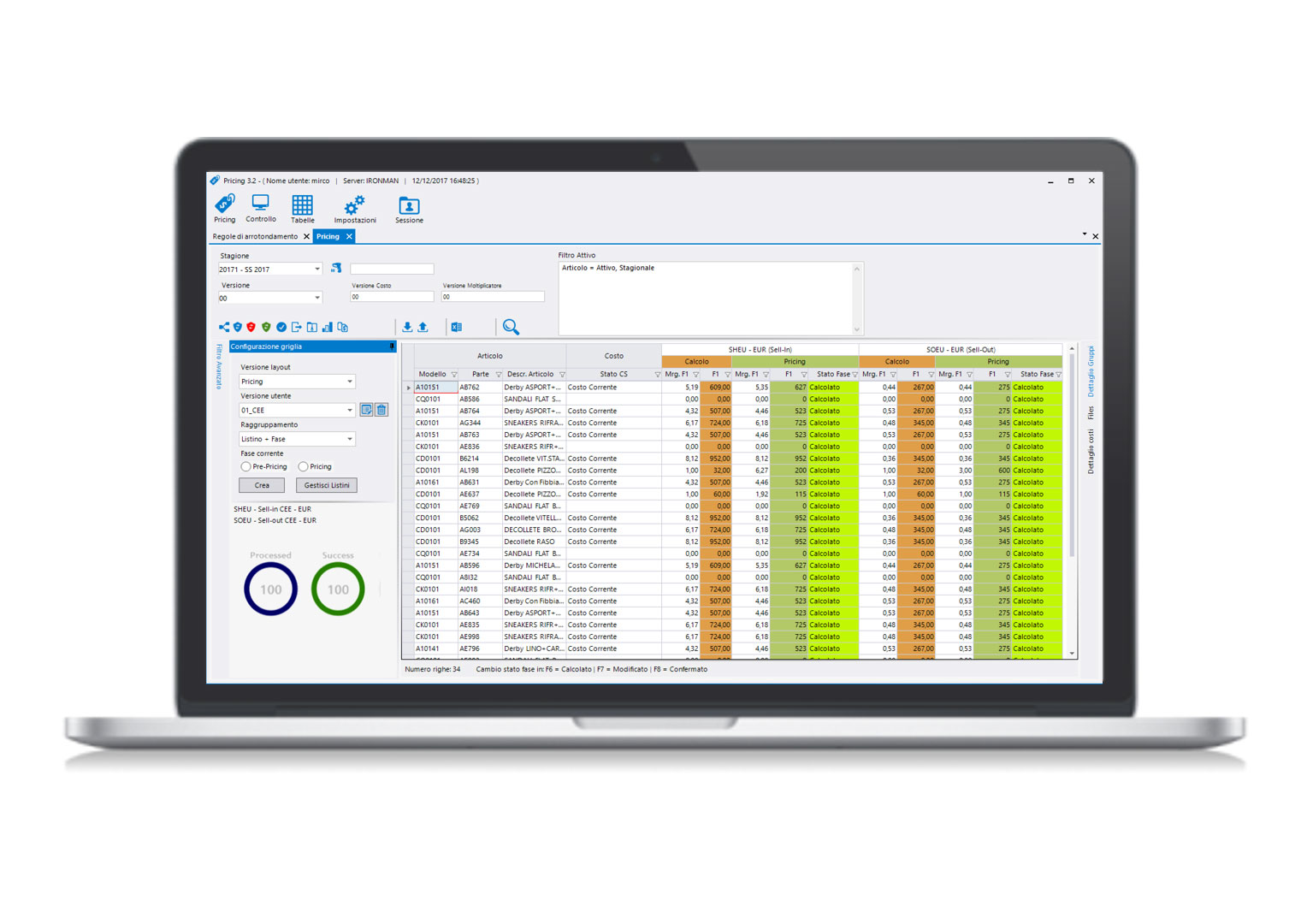
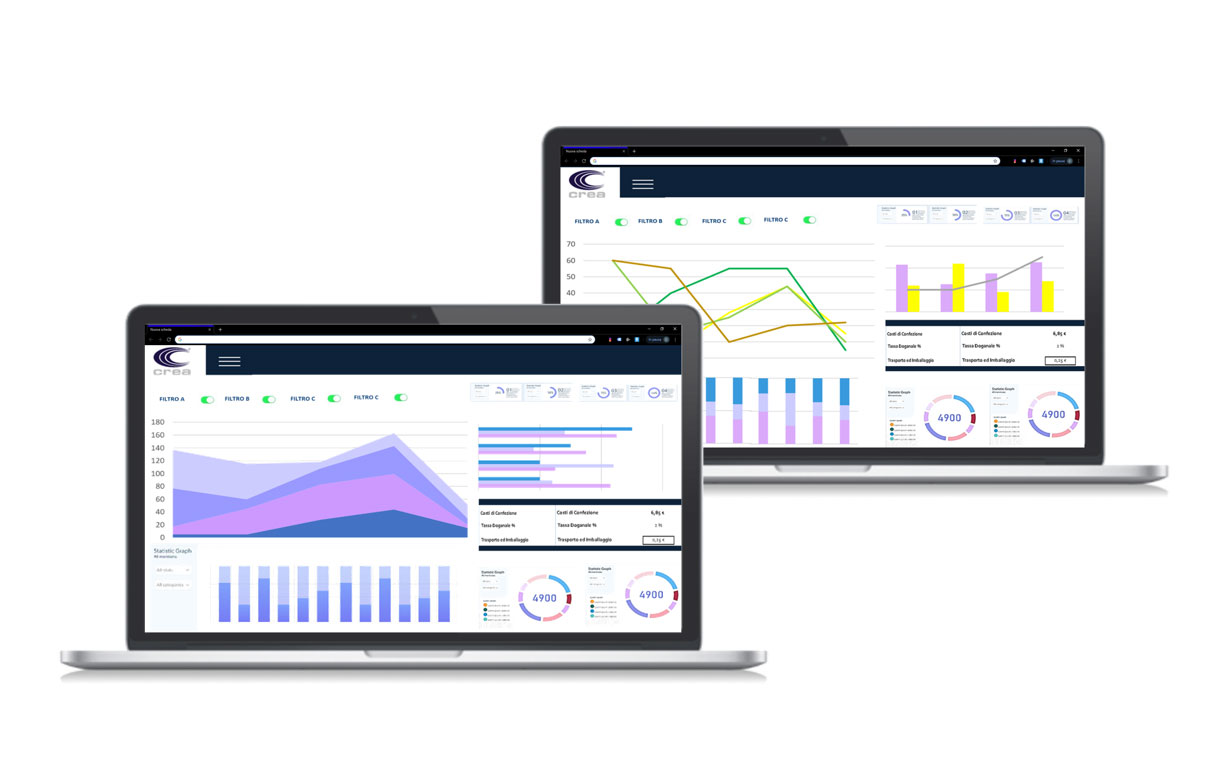
- Allows the historicization of data in order to verify the evolution and updates of these in the various phases of the product life cycle.
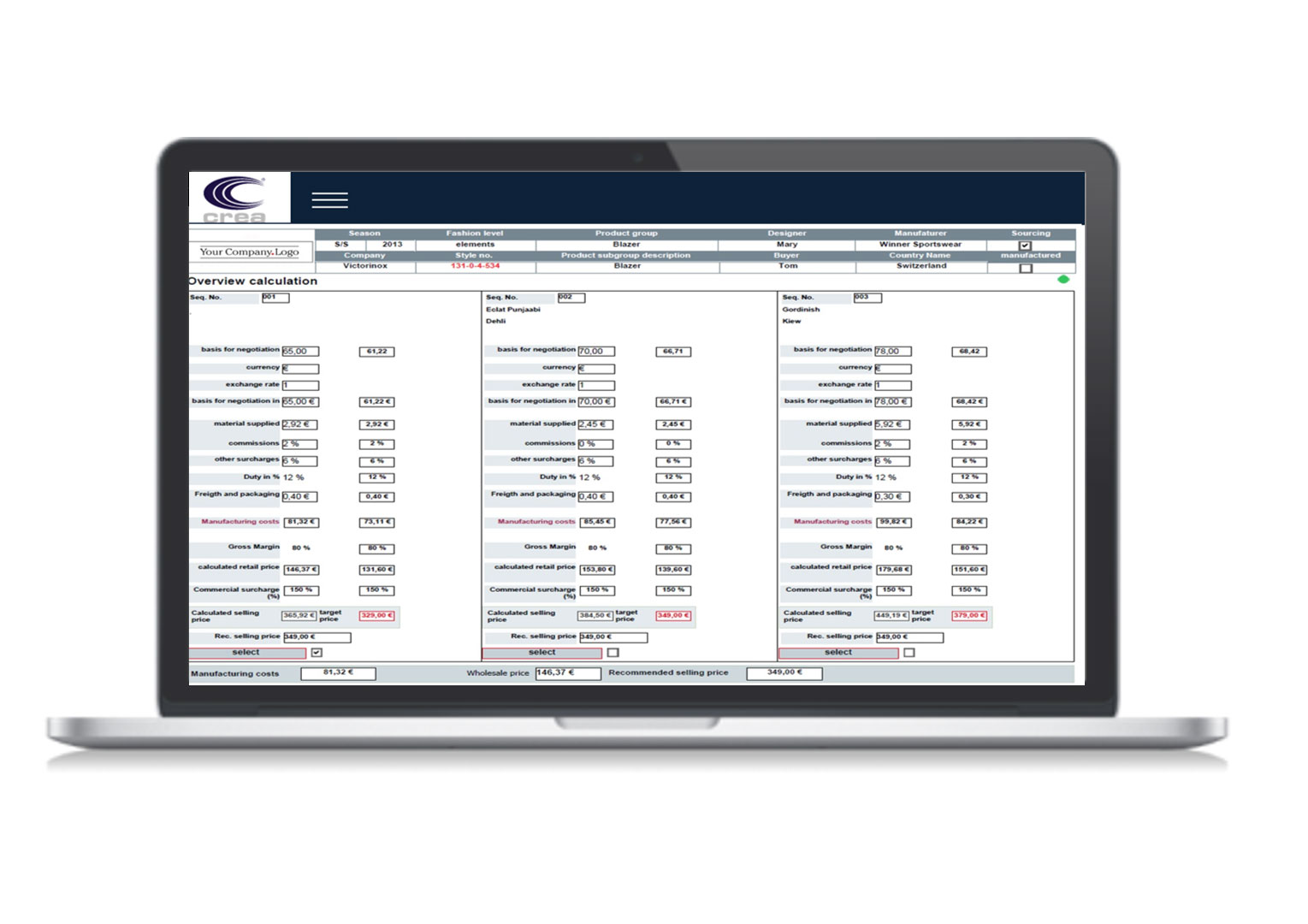
- Allows the storage of the technical specifications related to the product automatically in a database that regulates the business cycle of the same.
- Allows the interfacing and display of data related to archived documents thanks to the use of lightweight and portable formats (for example, in Adobe ™ PDF format or, for vector CAD format, in Autodesk ™ DWF) so as to facilitate the exchange of the same outside the company.
An important feature, linked to the modus operandi already seen years ago with the PDM (acronym for Product Data Management, which will be discussed shortly), is the link between metadata, usually stored on a structured database, and the documents, usually archived on system file (file system). This functionality allows an easy creation and implementation of automatic processing with the consequent launch of actions that also involve thousands of documents.
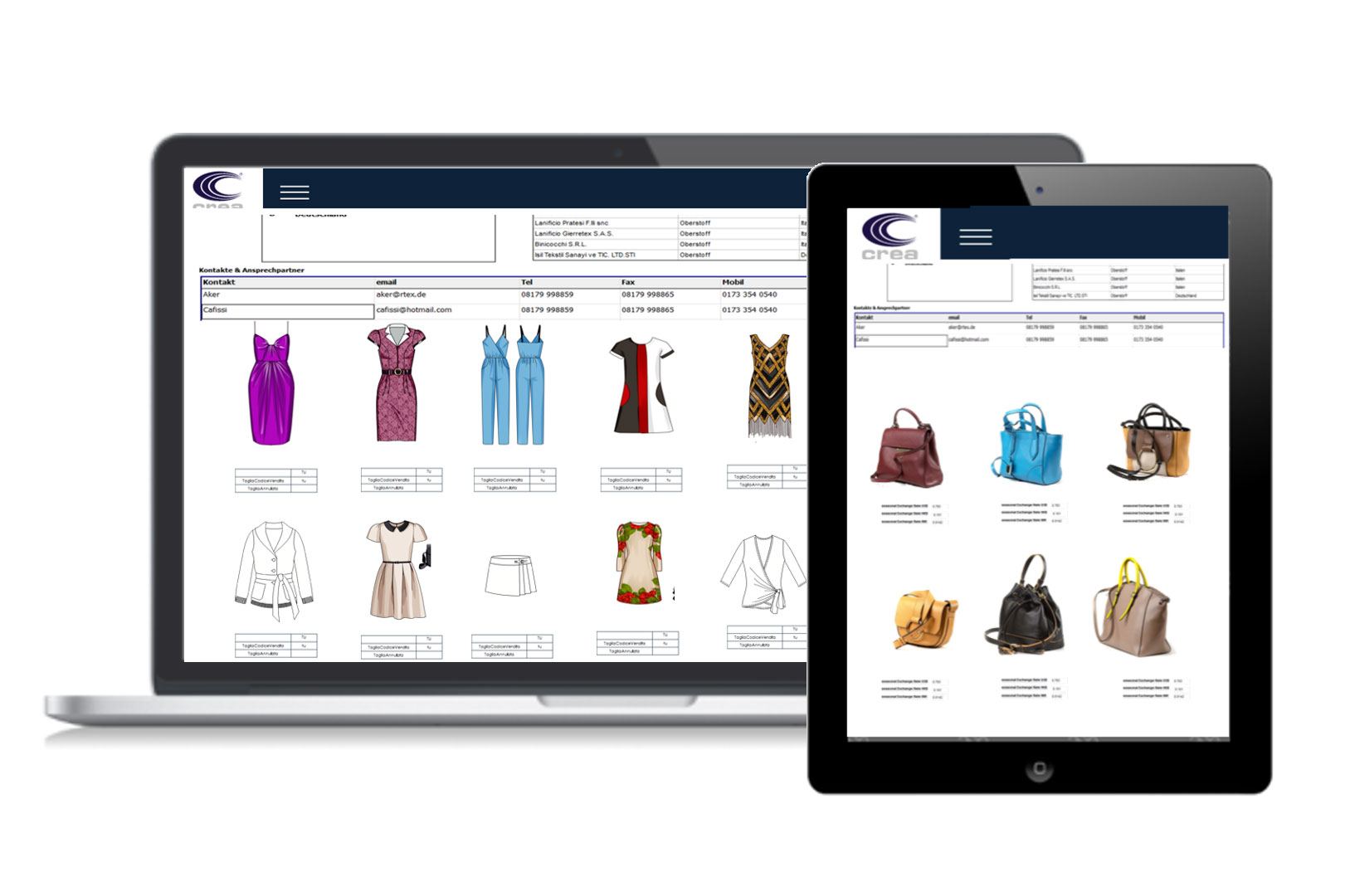
A central database is the fundamental heart of PLM software to ensure organized and always updated real-time data. The system allows the user to enjoy the entire data archive in a simple and quick way. For example, during the compilation of a new technical sheet it is possible to return to the drawings and 2D models of the garments in order to recover and reuse some sketches with floral motifs stored in the database before time, or the miniature of the pieces composing the 2D model of the head of interest. In the absence of a PLM system, the image files of those floral motifs or the model file would probably be stored in a local station of the stylists or modellers who created them making it much more difficult, sometimes impossible if the folders are not on the network and shared, their identification and their recovery.
PLM allows you to store and organize drawings, models, projects, documents and more in a systematic manner on one or more central servers so that anyone can access them. In this way a company can rely on a central system instead of on individual individual memories.
With PLM software, designers and modelers can make multiple changes quickly, allowing new designs, models and projects to be introduced or small drawings, models and projects already made in the past, stored in the archive, which are sold well on the base. statistics and cost estimates.