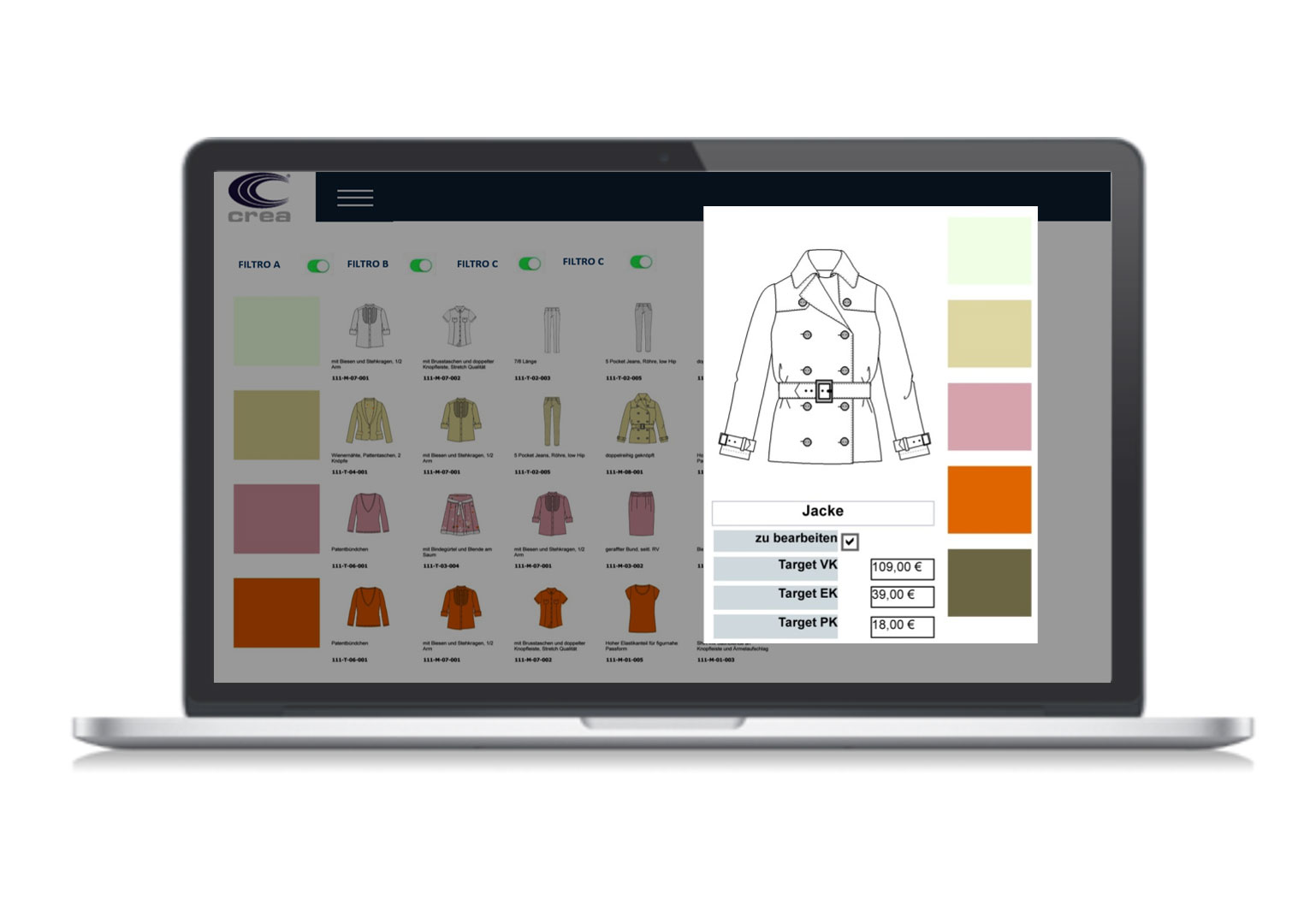
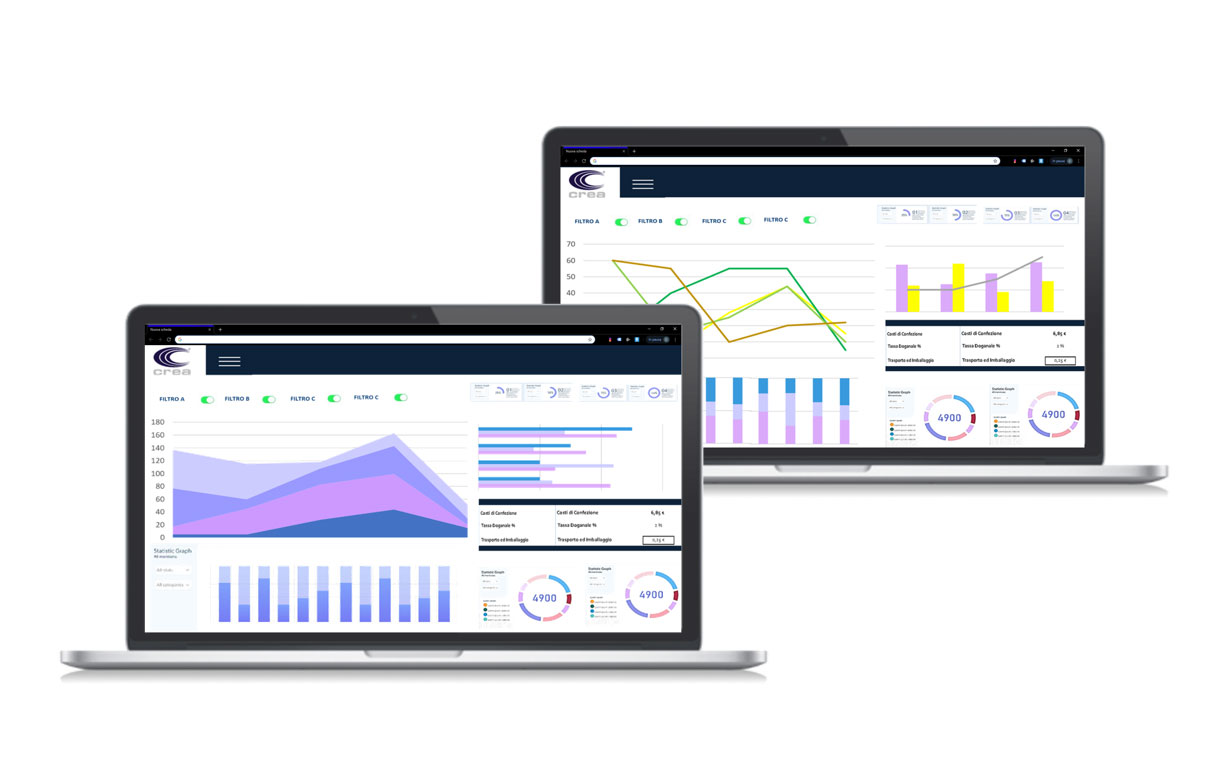
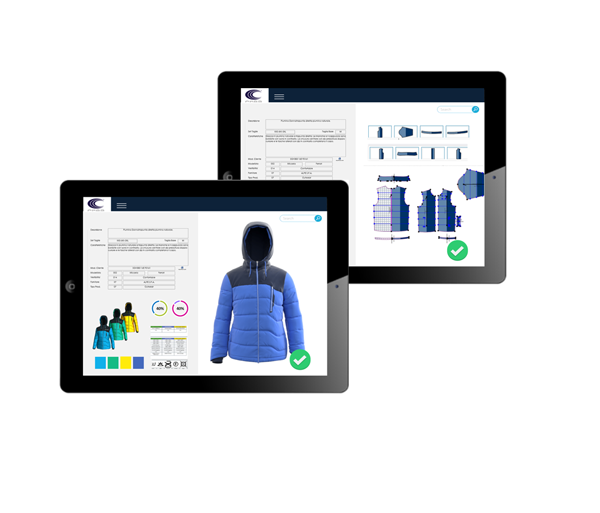
Textile Production: Key Processes to Know If You Work in the Fashion Industry
Textile production is one of the most crucial stages in creating clothing and other fashion-related products. This process, which consists of several stages, begins with fiber processing and ends with the finishing of the final product. If you work in the fashion industry, understanding each step of textile production allows you to optimize your projects, improve product quality, and reduce costs. In this article, we will explore the key processes of textile production, focusing on each phase that contributes to the creation of fabrics and finished garments.
1. Fiber Processing: The Foundation of Textile Production
Textile production starts with fiber processing. Each type of fiber—whether cotton, linen, hemp, or wool—requires specific treatments to be transformed into a material suitable for spinning.
• Cotton: Cotton production begins with harvesting cotton bolls from the plant. These are then separated from impurities through the ginning process, where the cotton is combed and prepared for spinning.
• Linen and Hemp: The processing of linen and hemp involves a series of retting and spinning processes that produce soft yet durable fibers, ideal for making long-lasting fabrics.
• Wool: Wool production starts with sheep shearing. After shearing, the wool is washed to remove impurities and grease. It then undergoes carding, a process that aligns the fibers and prepares them for spinning.
 2. Spinning: Transforming Fibers into Yarn
2. Spinning: Transforming Fibers into Yarn
Spinning is a crucial phase in textile production, where processed fibers are transformed into yarns. This step is essential in determining the type of fabric to be created. The main spinning processes include:
• Carded Spinning: Wool is carded to achieve a softer consistency. The fibers are aligned, and impurities are removed. Short fibers (“noils”) are reused to enhance the material.
• Combed Spinning: Here, fibers undergo further processing through a combing machine, which removes short fibers and better aligns the long ones, creating a smoother and more durable yarn.
During spinning, different types of yarn twists are also chosen, influencing the final texture of the fabric.
3. Fabric and Knitwear Production: Processing the Semi-Finished Material
Once the yarns are ready, the production of fabrics or knitwear begins. In this stage, yarns are woven, knitted, or processed into the final fabric. The type of weave, thread count, and density determine the fabric’s strength, softness, and appearance. Machines used include looms for weaving and knitting machines, enabling the creation of a wide range of materials for clothing and home textiles.
4. Difference Between Warp and Weft
In weaving, warp and weft are two fundamental elements that define the structure and look of a fabric.
• Warp: The set of threads arranged lengthwise (vertically) on the loom. These threads are stretched and provide the structural foundation of the fabric.
• Weft: The threads woven transversely (horizontally) through the warp. The weft is inserted across the warp to create the final fabric.
The combination of warp and weft, along with the weave type, determines the texture, elasticity, and durability of the fabric. For example, a tight weave results in a more resistant fabric, while a looser weave makes it lighter and more breathable.
5. Finishing: Enhancing the Final Product
Finishing is the last phase of textile production and includes various treatments that improve the fabric’s aesthetic and functional characteristics. The main finishing processes include:
• Dyeing: The dyeing process applies color to the fabric. Dyeing can be done before or after weaving, depending on the desired result.
• Printing: In this stage, patterns, designs, and decorations are applied to fabrics. Common techniques include screen printing, digital printing, and heat transfer printing.
• Cutting and Sewing: Once the fabric is finished, it is cut and sewn into various garments, accessories, or home textile products.
Each finishing step helps achieve a high-quality final product, ready to be sold on the market.
Textile production is a complex process involving multiple stages, from fiber processing to finishing the final product. Each phase contributes to determining the quality of the fabric and, ultimately, the finished garment. Understanding every aspect of textile production is essential for those working in the fashion industry, both to optimize production times and to ensure high-quality products.